
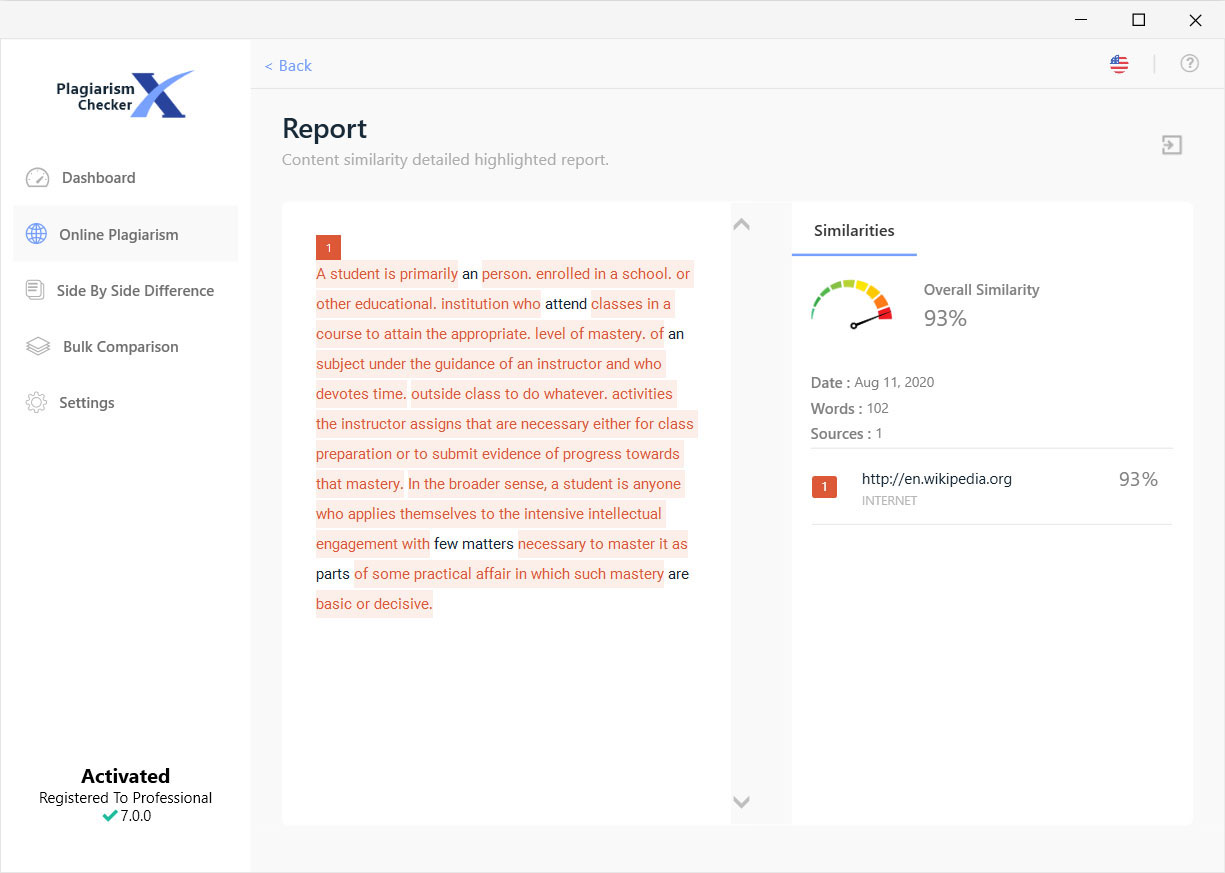
To determine the percentage of duplication in your document we are analyzing the sentence structure of your text and then searching billions of documents and web resources for similarities to your input. Cases of accidental imitation are taken as seriously as any other theft and are subject to the same consequences as other types. Lack of intent does not relieve the student of responsibility for stealing. Students should learn to quote their sources and make accurate and accurate notes when conducting research. This also refers to submitting the same work to complete assignments in different classes without the prior permission of two teachers.Īccidental plagiarism occurs when a person neglects references to his sources or incorrectly quotes their sources or unwittingly paraphrases the source using similar words, groups of words, and/or sentence structure without attribution. For example, it would be unacceptable to include some of the class work you wrote in high school in a book assigned to a college class. Self-plagiarism occurs when a student submits their previous work or mixes parts of previous work without the permission of all participating teachers.
Sometimes called a “correction,” this type of paraphrase, whether intentional or not, is academically dishonest and punishable - even if you make a footnote to your source! Mosaic plagiarism occurs when a student borrows phrases from a source without using quotations or finds synonyms for the author’s language while maintaining the same general structure and meaning of the original. The intentional stealing of someone else's work is unethical, academically dishonest and the basis for disciplinary action, including expulsion.
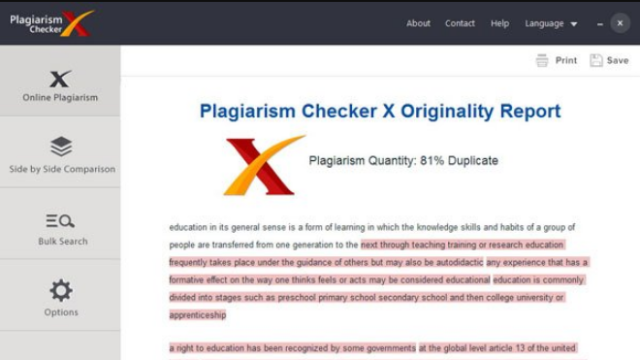
Direct plagiarism is the literal transcription of part of someone else’s work, without attribution and quotation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
